Water Treatment Systems
We offer systems for customers ranging from residential applications to complex municipal and industrial systems. Our experienced staff can help you diagnose and solve all of your water problems. We stock most residential solutions for common problems like:
- Hardness
- Iron
- Manganese
- pH
- Odors
- Discoloration
- Hydrogen Sulfide (rotten egg smell)
- Bacteria
- Taste
- TDS
Water Softeners
 Softeners are effective at removing hardness, small amounts of ferrous iron (clear water) and small amounts of manganese. They do not treat for ferric iron (red discolored water), adjust pH or remove odors. Customer maintenance is required to add salt to a brine tank as necessary. Two types of softeners are available (Time Clock and Metered) with a capacity of one cubic foot and above. Time Clock units perform a backwash of the system based on a set number of days (not volume of water processed). Metered units backwash based on the amount of water passing through the system and are therefore, more effective in maintaining water quality. Metered units are available in single and twin tank configurations. Twin tank applications use filtered water for the backwash cycle by having one tank in service and one in standby. Then when a backwash is required the water supply switches the two tanks – service tank becomes standby and the standby becomes the service tank.
Softeners are effective at removing hardness, small amounts of ferrous iron (clear water) and small amounts of manganese. They do not treat for ferric iron (red discolored water), adjust pH or remove odors. Customer maintenance is required to add salt to a brine tank as necessary. Two types of softeners are available (Time Clock and Metered) with a capacity of one cubic foot and above. Time Clock units perform a backwash of the system based on a set number of days (not volume of water processed). Metered units backwash based on the amount of water passing through the system and are therefore, more effective in maintaining water quality. Metered units are available in single and twin tank configurations. Twin tank applications use filtered water for the backwash cycle by having one tank in service and one in standby. Then when a backwash is required the water supply switches the two tanks – service tank becomes standby and the standby becomes the service tank.
City Water Softeners / Dechlorinationg Softeners
By adding carbon to the resin inside the tank these units provide the same benefits stated above plus the benefits of a carbon filter (see Carbon – under filters below). However, replacement of the resin and carbon will be required when depleted. The lifespan of the carbon caries by application. For further information, please contact us.
Manganese Greensand Filters
Greensand filters utilize a potassium permanganate regenerate to oxidize and filter moderate levels of iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide. There application requires a pH of 6.8 or higher. These filters are available in sizes from one cubic foot and above.
Backwash Filters
 We offer various types of backwashing filters: Carbon, Filter-Ag, Sand, Birm, Neutralizing media (some blended media).
We offer various types of backwashing filters: Carbon, Filter-Ag, Sand, Birm, Neutralizing media (some blended media).
Carbon – commonly referred to as “taste and odor” filters. They are effective at removing/reducing volatile organic chemicals (VOC), pesticides and herbicides, chlorine, benzene, trihalomethane (THM), radon, and many other man made chemicals. It is effective at removing/reducing sediment, ferric (red water) iron, manganese, and hydrogen sulfide (rotten egg smell) but with a shorter life span than with the previously listed contaminants. Carbon filters are NOT effective at removing inorganic contaminants, metal, salts, hardness, arsenic, copper, nickel, nitrates/nitrites, and sulfates. Carbon should be replaced according to schedule. Carbon should always be replaced annually, unless it is being used for chlorine removal.
Filter-Ag – is silica, crystalline quartz media, which can be used as highly efficient filter media for the reduction of suspended matter. It filters oxidized iron, manganese, and sediment down to the 20-40 micron range. It has a higher flow rate than filter sand, and it is easier to backwash. It is effective over a wide range of pH values.
Sand – is an effective filter media used for the removal/reduction of ferric (red water) iron, oxidized manganese, and sediment. Various sand sizes can be used to achieve the desired filtration size.
Birm – is a media that removes iron and manganese. It requires a high dissolved oxygen content in the water to work correctly.
Neutralizers – contain a Calcite and Corosex blended media. As the acidic water flows through this media, the media is slowly dissolved and raises the pH. As this occurs, hardness is added to the water. A softener generally follows neutralizers. They also filter out some ferric (red water) iron. Frequent backwashing is required to prevent the media from packing or cementing together. It is not recommend to use neutralizers on waters with a pH below 6.2. When the pH is below 6.2, we feel neutralizers require too much maintenance.
Chlorination Systems
This type of system is used for the removal of iron, sulfur, manganese, algae, and bacteria. These systems utilize a feed pump to inject a solution of chlorine (most commonly household bleach mixed with water) into the water supply. The water then flows through a fiberglass contact tank. This gives the chlorine time to react with the water. After the chlorine has reacted with the water, it then goes through a filtration process (usually a Filter-Ag or carbon backwashing filter).
UV Lights
Ultraviolet lights are used for disinfection. They kill bacteria and viruses. Ultraviolet lights are popular because of the low maintenance and the fact that they do not add any chemicals to the water, but the incoming water must be clear. There are various options available depending on the required flow rate. The bulb must be replaced annually to ensure the light is effective.
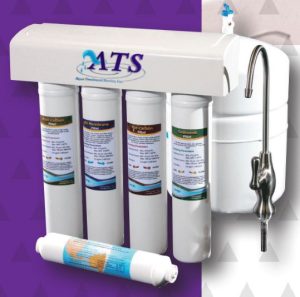 Reverse Osmosis (RO)
Reverse Osmosis (RO)
Reverse Osmosis is a commonly used method of treatment for drinking water. Reverse Osmosis uses pressure to force water molecules through a semi-permeable membrane. Ions and larger molecules are not able to pass through the membrane. The incoming water supply should be free of hardness, iron, and manganese. RO units have multiple steps. Most include a sediment filter, carbon filter, RO membrane, and carbon post filter. The sediment, carbon, and post filters should be replaced annually. The membrane should be replaced once it has dropped below its minimum efficiency.
